Customization:
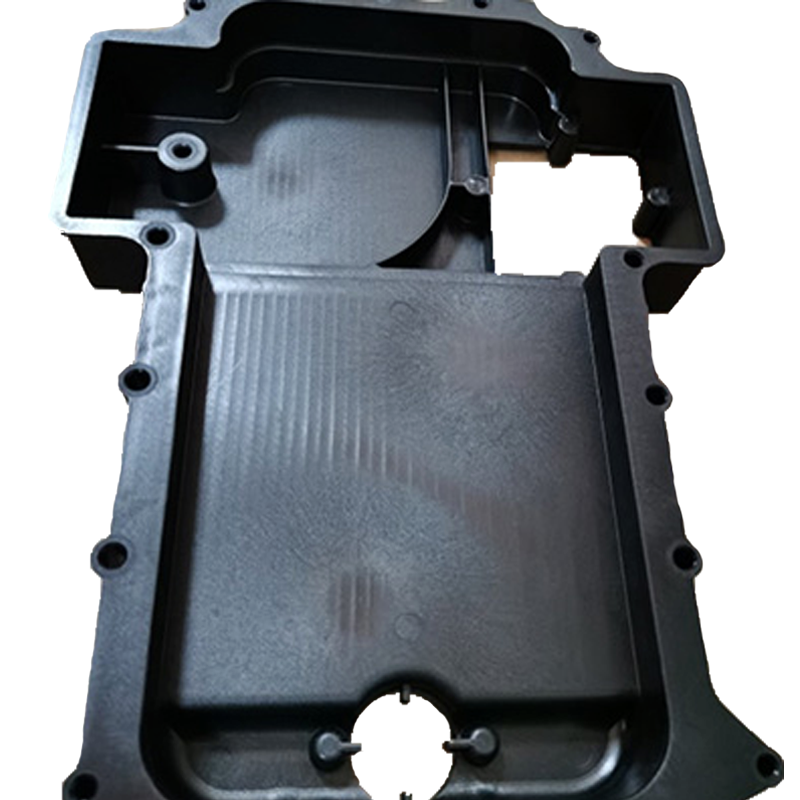
Application customization: Part design tailored to automotive hydrogen fuel cell stacks
Material selection expertise: High-temperature polymer material selection and recommendations
Engineering design optimization: Fluid dynamics analysis and performance enhancement
Precision manufacturing process: High-precision injection molding and two-shot molding techniques
Flame retardant considerations: Meeting international flame retardant standards
Rigorous quality control: Comprehensive quality inspections and material testing
Environmental sustainability solutions: Material recycling and energy-efficient processes
On-time delivery commitment: Adherence to project timelines
Technical support and continuous improvement: Professional support for design optimization, problem resolution, and ongoing performance enhancement
Basic process of mold building:
| Product pre-analysis | 1.Part Injection molding Feasibility Analysis(DFM) 2.Run mold flow analysis |
| Mold design | A. Specific 2D assembly drawing B. 3D assembly drawing C. Drawing of parts and loose items D. Mold BOM sheet and purchase order |
| Mold making | A. Release of drawings B. CNC mold core C. Mold and accessory processing D. Mold assembly |
| Mold Trial | A. Material and machine preparation B. Making samples with machines C. Mold testing report |
| QI | A. Product dimensions and assembly test B. Product improvement report C. Functional test and improvement report |
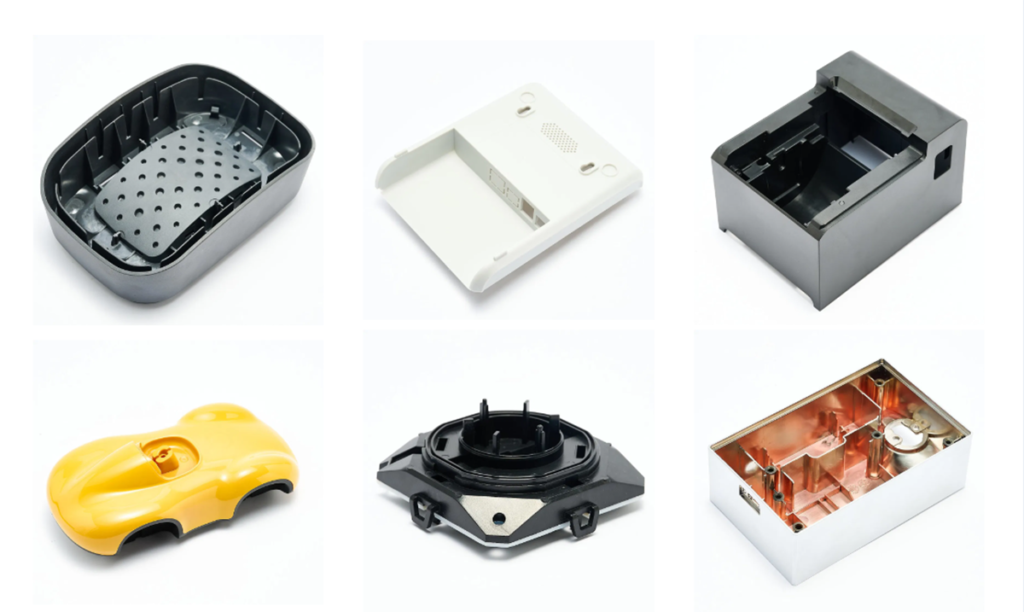
More Plastic Injection Shell Box

The material selection requirements for the Hydrogen Fuel Cell Injection Molded Plastic Part are as follows:
- High-Temperature Resistance: Due to the typically elevated operating temperatures of hydrogen fuel cell systems, the selected material must exhibit excellent high-temperature resistance to maintain stability and performance in high-temperature environments.
- Chemical Corrosion Resistance: Hydrogen fuel cells involve hydrogen gas and chemical reactions, so the chosen material must withstand chemical corrosion to ensure long-term durability.
- Mechanical Strength: The part needs to have sufficient mechanical strength to withstand internal system pressures and external stresses, ensuring it does not deform or become damaged.
- Dimensional Stability: The material must demonstrate dimensional stability to ensure that the part’s dimensions remain consistent under varying temperature and humidity conditions, preventing fluctuations.
- Lightweight Design: When selecting materials, priority should be given to lightweight design to reduce the part’s weight, thereby enhancing overall energy efficiency and reducing the load.
- Flame Retardance: As the part may come into contact with hydrogen gas, the selected material should possess flame-retardant properties to mitigate the risk of fire.
- Long-Term Stability: The material should exhibit long-term stability to ensure that the part maintains performance over years of use, reducing the need for replacement and maintenance.
- Sustainability: Consider selecting sustainable materials to align with environmental and sustainability standards while reducing reliance on finite resources.